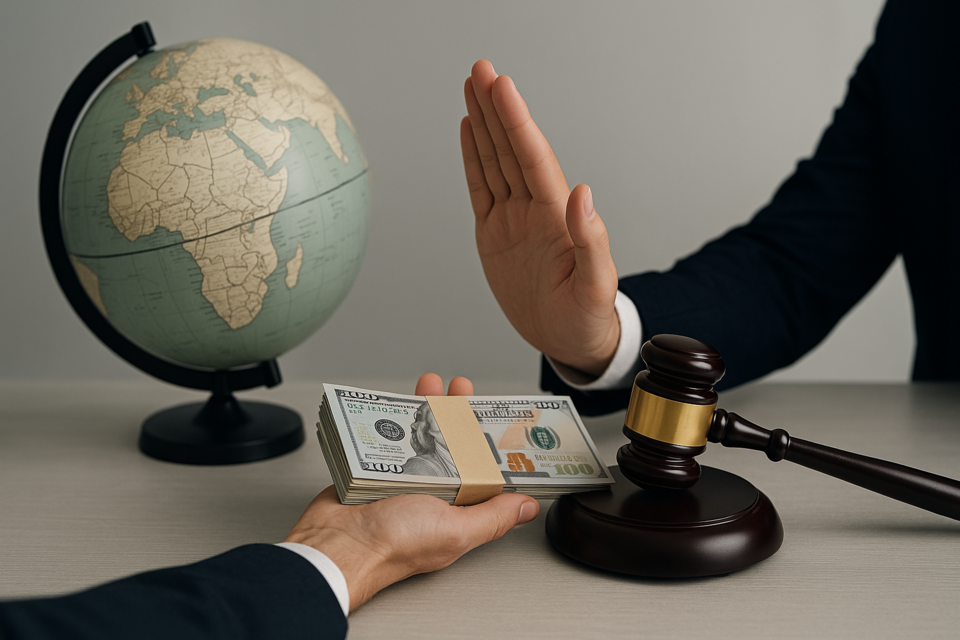
Global Anti-Corruption and Bribery
Empower Change, End Corruption.

10 Hours average completion time
1.0 CEUs
15 Lessons
31 Exams & Assignments
5 Discussions
39 Reference Files
119 Articles
Mobile Friendly
Last Updated January 2026
Combating Bribery and Corruption in Modern Business
In an era where headlines often shout of corporate scandals and shadowy deals, the integrity of business comes under scrutiny. Bribery and corruption, while offering a deceptive advantage, can undermine the very fabric of commerce, society, and global peace. But what if you could be the change-maker? What if you could not just navigate the labyrinth of regulations but also champion the cause for a transparent business world?
Welcome to our course, tailored to empower individuals and businesses with the knowledge and tools to combat bribery and corruption.
Here's your journey with us:
-
Global Perspectives: Dive deep into the regulations governing bribery and corruption in powerhouse nations like the United States and the UK, and then span out to grasp global trends and norms.
-
Mastering Anti-Corruption: Understand the backbone of anti-corruption compliance programs. Learn how they serve as shields against murky practices and potential liabilities.
-
Building Fortresses: Familiarize yourself with the mechanisms and controls that thwart corrupt practices. Design your blueprint for an iron-clad anti-corruption compliance program.
-
Risk Mapping: Equip yourself with skills to conduct comprehensive corruption risk assessments and audits, ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly.
-
Beyond Business: Explore the intriguing nexus between corruption, organized crime, and global terrorism, understanding the broader implications of unchecked corruption.
To ensure an engaging and structured learning experience, the course unfolds over fifteen meticulously crafted lessons. Each module culminates in a thought-provoking exercise, allowing you to gauge your grasp over the content. These assessments are crucial touchpoints in your journey, leading you to a triumphant completion.
Are you ready to be the torchbearer of integrity in the business world? Enroll today and embark on a transformative journey towards ethical excellence!
- Conducting Comprehensive Risk Assessments
- Advanced Political and Legal Analysis
- Strengthening Corporate Governance Practices
- Global Anti-Corruption Strategy Development
- Understanding International Anti-Bribery Laws
- Improving Fraud and Audit Capabilities
- Enhancing Organizational Regulatory Compliance
- Building Robust Compliance Programs
- Cross-Cultural Ethical Decision Making
- Investigating Bribery and Corruption Incidents
- Identifying Emerging Corruption Trends
-

Management Essentials
-

Financial Analysis 101: Planning and Control
-

Lean Management
-

Business Coaching
-

Accounts Receivable Training
-

Business Consulting 101
-

Leadership Skills for Managers
-

Strategic Planning
-
Business Budgeting 101: How to Plan, Save, and Manage
-

Business Etiquette
-

Habits of Millionaires
-

Writing Help Course Bundle
-

Sustainable Development for Business
-

Modern Marketing Strategies for Small Business
-

Product Management 101
-

Kaizen 101 - An Introduction
-

Introduction to Ethics
-

Business Credit 101
-

Marketing 101
-

Ultimate Secretary Training Bundle
-

Legal Terminology 101
-

Accounting & Bookkeeping 101 for Everyone
-

Business Analysis
-

Business Ethics
-

Marketing Outreach
