| Grouping of Objects |

| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 |
| 4 Dogs | 4 Dogs | 4 Dogs |
12  3 = 4 (here we use the division symbol)
3 = 4 (here we use the division symbol)
| Terms � Divisor, Dividend, Quotient, Remainder |
There are four main terms to describe the parts of division. The dividend is the number that is being divided. The divisor is the number that will be doing the dividing. The quotient is the answer, or the number of times the divisor goes into the dividend. In the problem, 12  3 = 4, 12 is the dividend, 3 is the divisor and 4 is the quotient.
3 = 4, 12 is the dividend, 3 is the divisor and 4 is the quotient.
If we have the problem 23  5 = 4 R 3, we have a dividend of 23, a divisor of 5, a quotient of 4, and a remainder of 3 because 23 cannot be divided equally into 5 groups. When you divide it into 5 groups, you get 4 in each group and 3 objects left over.
5 = 4 R 3, we have a dividend of 23, a divisor of 5, a quotient of 4, and a remainder of 3 because 23 cannot be divided equally into 5 groups. When you divide it into 5 groups, you get 4 in each group and 3 objects left over.
| Division Facts |
Division is quicker and easier once you know and memorize the basic facts. The division facts are the inverses of the multiplication facts. For example, if 9 x 6 = 54, then 54
 9 = 6.
9 = 6. Flash cards are a great aid in learning division facts.
| Division by Zero - Undefined |
Division is defined as the inverse of multiplication. If 2 x 9 = 18, then 18
 9 = 2 and 18
9 = 2 and 18  2 = 9.
2 = 9.Division by zero would be the inverse of multiplying by zero. 7 x 0 = 0. This corresponds to 0/7 = 0 or 0  7 = 0. However, 0
7 = 0. However, 0  0 is not 7. This does not compute. So division by zero is undefined since it does not work with our definition.
0 is not 7. This does not compute. So division by zero is undefined since it does not work with our definition.
Division of zero is considered undefined. It is impossible to divide nothing into groups of nothing.
| Multiplication Identity Element - One |
An identity element is a specific number that when put with any other number in a specific way gives the original number. One is the multiplicative or multiplication identity element. It is also a division identity element. One times any number is the original number; an original number divided by one is the original number.
a x 1 = a
5 x 1 = 5 and 25 x 1 = 25
A  1 = a
1 = a
5  1 = 5 and 25
1 = 5 and 25  1 = 25
1 = 25
| Multiplicative inverse |
A multiplicative inverse, or reciprocal, for a number (such as a) is denoted by 1/a such that the number, a, and its reciprocal, 1/a, yield 1 when multiplied.
For example, the multiplicative inverse of 8 is 1/8. When you multiply 8 x 1/8, the answer is 8/8 which is 1, or 1 whole.
For the multiplicative inverse or reciprocal of any number, divide 1 by that number.
| Division with a Single Digit Divisor |

We can ask: how many times does 2 go into 4 or 4 divided by what equals 2. We know that 2 x 2 = 4. Therefore, we put a 2 above the 4, then we multiply that 2 times the 2 in the divisor and get 4 which we put under the 4 and subtract.

When we subtract, the answer must always be less than the divisor. If it is not, you know that the digit you used in the quotient can be increased by at least one. Also check your multiplication and your subtraction.

To check your answer, multiply the quotient by the divisor. If the dividend is your answer, your quotient is correct. 2 x 23 = 46.
This is a fairly simple problem which works out evenly. Let's try a problem which is not so straightforward. Let's divide 3,749 by 3.



Now we need a number that when multiplied by 3 gives us the closest number to 14 without going over. 3 x 5 = 15, so that is too much. 3 x 4 = 12, so we use 4 above the 4, and put the 12 under the 14 and subtract to get 2. Then we bring down the 9.

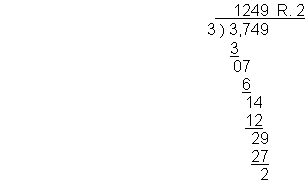
In real life situations, a remainder does not work out very well. When you start to do decimals, you will use another method to work with remainders.
To check your answer, multiply the quotient by the divisor, then add the remainder:
| Division with a Multiple Digit Divisor |
Sometimes your divisor has two or three digits. This really isn't difficult to work with; it simply takes a little more thought. Let's look at 2,892
 12.
12.


This is the same number as our divisor, so we put a 1 (multiplicative identity element) above the 2, multiply and subtract to get 0.

| Divisibility Rules |
1. A number is evenly divisible by 2 if it ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8.
2. A number is evenly divisible by 3 if the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3.
3. A number is evenly divisible by 4 if the lasts two digits are a number that is a multiple of 4.
4. A number is evenly divisible by 5 if it ends with 5 or 0.
5. A number is evenly divisible by 6 if the sum of the digits of the number is a number that is a multiple of 3 and the last digit is an even number (divisible by 2).
6. A number is evenly divisible by 9 if the sum of the digits are a multiple of 9.